
Dear Friends,
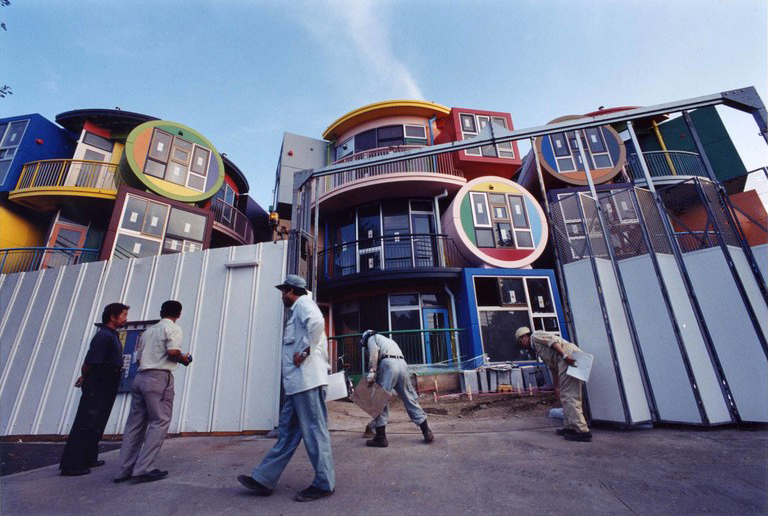
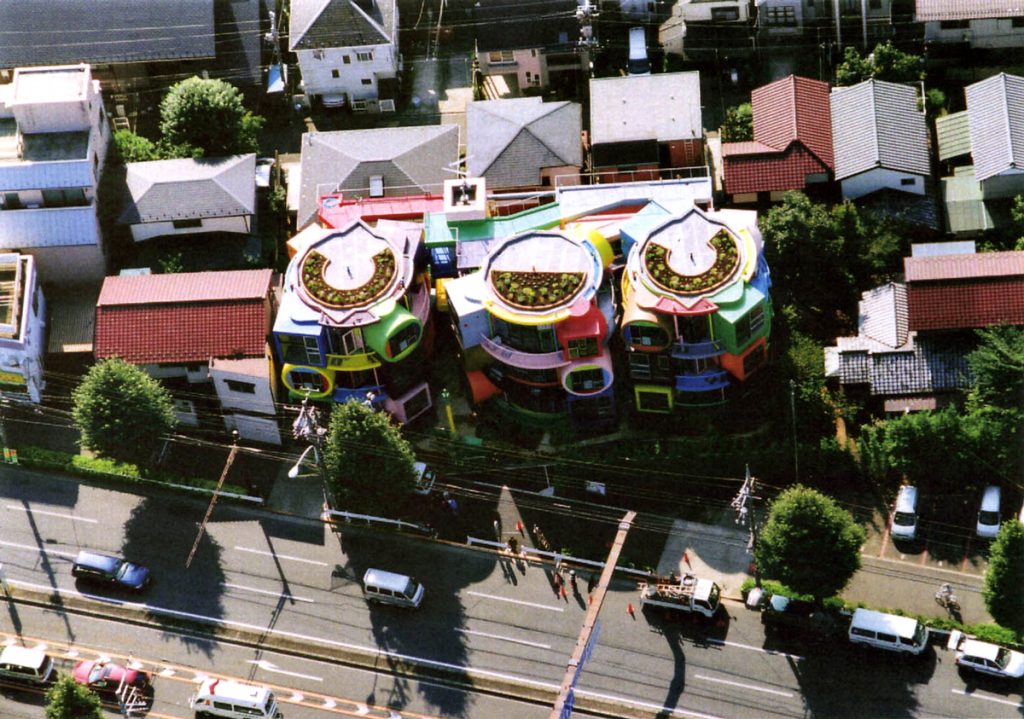
Did you know that today, October 15th, is the official “birthday” of the Reversible Destiny Lofts—Mitaka (In Memory of Helen Keller) in Tokyo? Designed by Arakawa+Gins and completed on this day in 2005, it is one of the most unique apartment buildings in Japan. There are a total of nine units in the building: five of them are currently occupied by tenants, two are offered for short-term stays and remote work space programs as well as group tours, events, and workshops, and the last two units house the ARAKAWA+GINS Tokyo Office, which manages all aspects of the operations there. The Mitaka Lofts has attracted thousands of people from around the world, many of whom have made a special pilgrimage to experience the space in person. At the time of its opening 16 years ago, people were beguiled by it and they hotly debated whether this was architecture or art. Arakawa+Gins’s vision, however, was clear that this was to be a residential building, inhabited and used by people. Through this creation, they aspired to change Japan and even the whole world.
In this third edition of Ambiguous Zones, we share with you the “making of” the Reversible Destiny Lofts—Mitaka accompanied by a selection of architectural renderings and photographs that attests to its distinctive and complex construction.
Because the building has received many thousands of visitors every year for the past 16 years, there is great need for repair and conservation. The Tokyo Office is gearing up for a global crowdfunding initiative, launching early next year* for this ongoing project of preservation, so please stay tuned for more information in the coming months. In the meantime, we hope that AZ3 will convey the significance of this actively lived and highly engaging work of Arakawa+Gins.
Yours in the reversible destiny mode,
Reversible Destiny Foundation and ARAKAWA+GINS Tokyo Office
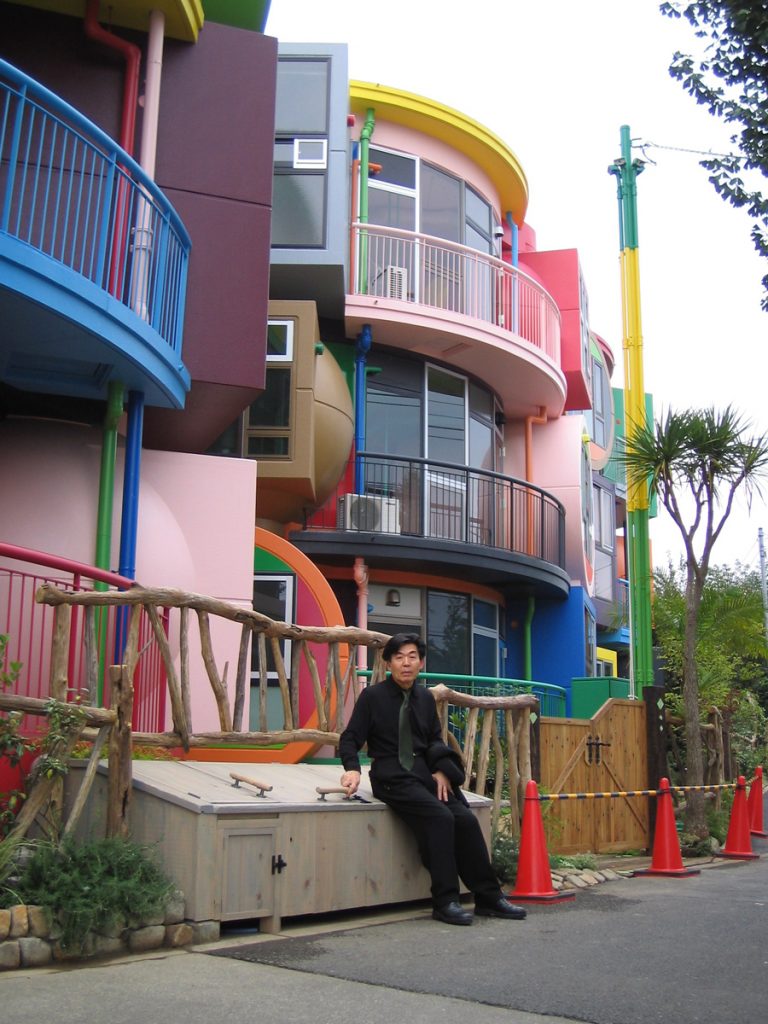

The main inspiration for the design of the lofts was Helen Keller. In what kind of space would she have wanted to live? Her life’s story taught us that each of our bodies is unique and we are all born with an individual ability to form and use its surrounding space and environment. The Mitaka Lofts, as an experiential laboratory, functions as a space that instructs us and our body toward boundless freedom. There are many architectural elements that are unusual, to say the least. One of the most distinct is the floor with a series of small bumps that constantly make you conscious of the sole of your feet and at the same time stimulate blood circulation. For the visually impaired, like Helen Keller, this feature helps them navigate the room.
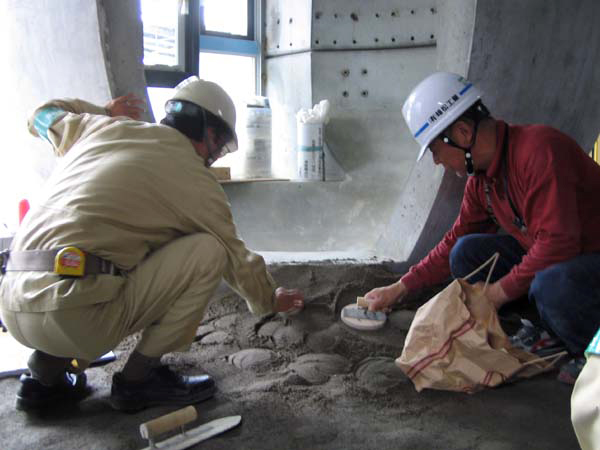


Other interesting components are floor-to-ceiling vertical poles that can have a variety of functions if you tap into your imagination. They can be exercise poles, ladders, shelves, and for people with walking difficulties, bars to grab onto that offer support as they move about in the space.
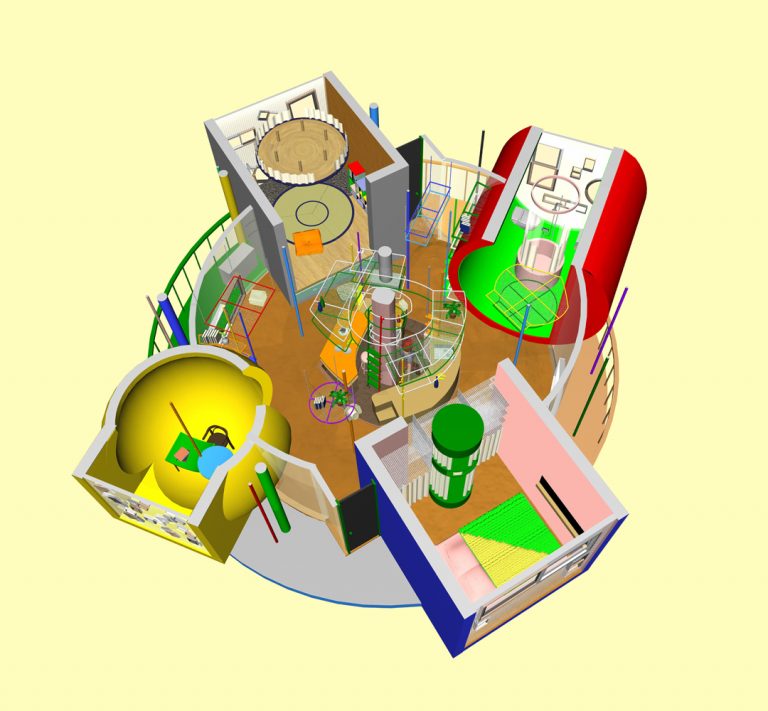
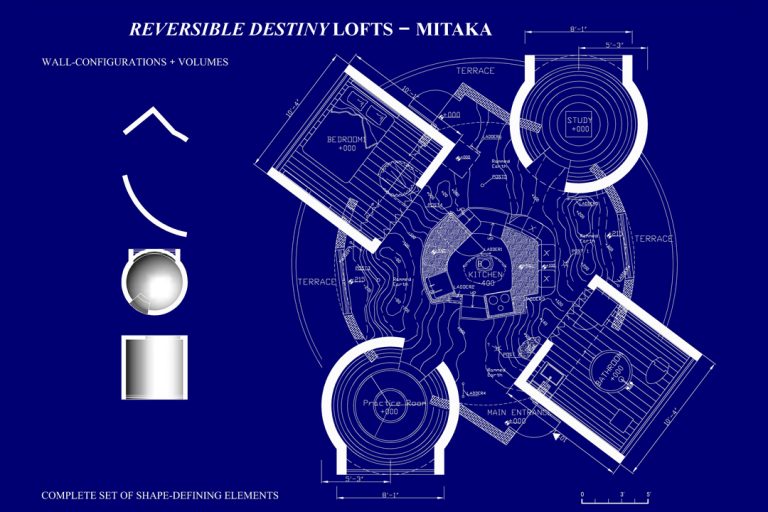
Because of the role that Helen Keller played in the ideation of the design, the Mitaka Lofts has been a focus of interest among scholars not only of art and architecture but also from the areas of welfare, medicine, and physical therapy. In addition, the creatives who are involved in product or environmental design for people with disabilities also pay attention to this building in order to activate the power of alternative thinking. In this way, A+G’s unconventional philosophy contributes to a building of an inclusive and cooperative society that the world needs today.
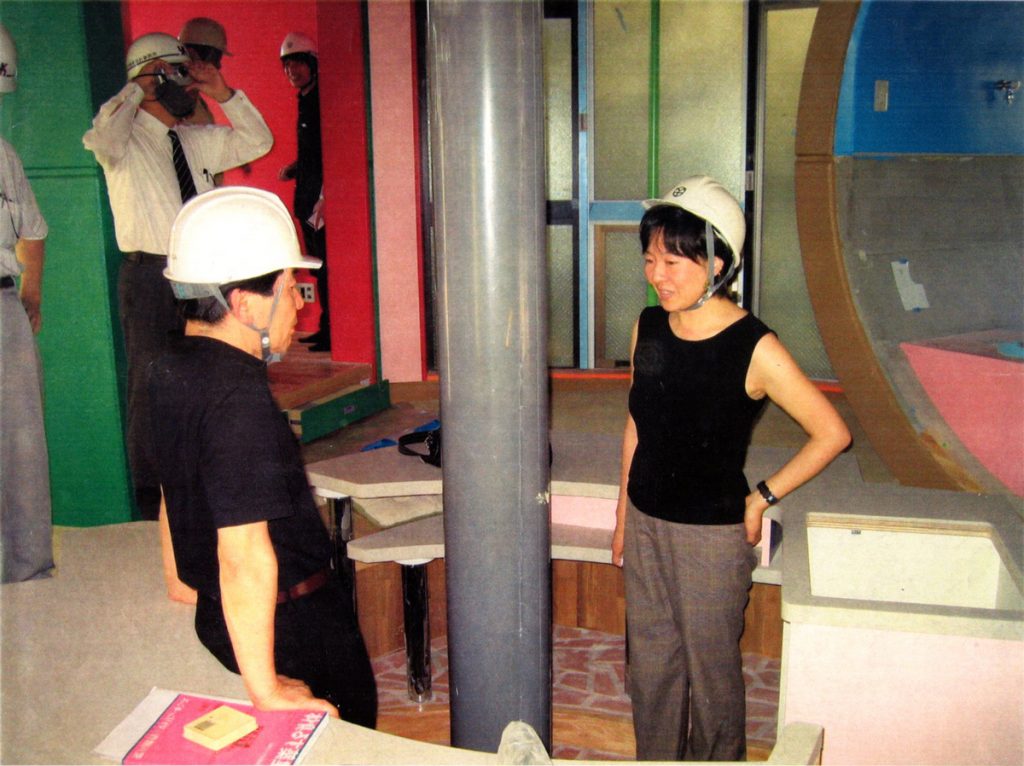
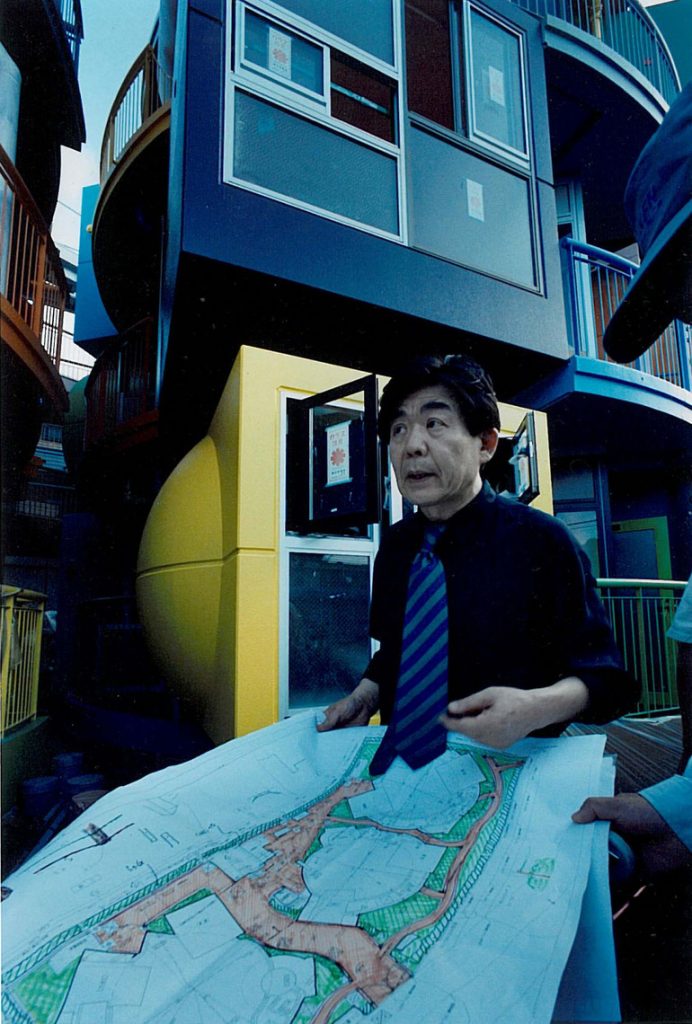
In their 2002 publication Architectural Body, Arakawa and Gins wrote that “although our species, like every other species, has a characteristic architecture that serves its members well by increasing their chances of survival, it is far from having an architecture that could redefine life. The architecture we speak of in this book is within our species’ reach. It will be a way to undo, loosening to widen and re-cast, the concept of person.”** Realizing such an architecture was an enormously complicated challenge. Knowing there was no precedent of this kind and driven by a singular passion, Arakawa visited a number of top executives of major construction companies in Japan. Ultimately, a dream team consisting of veterans of the field was formed in Tokyo to take on the task: Yasui Architects & Engineers, Inc. finalized the detailed design and Takenaka Corporation worked on the construction.
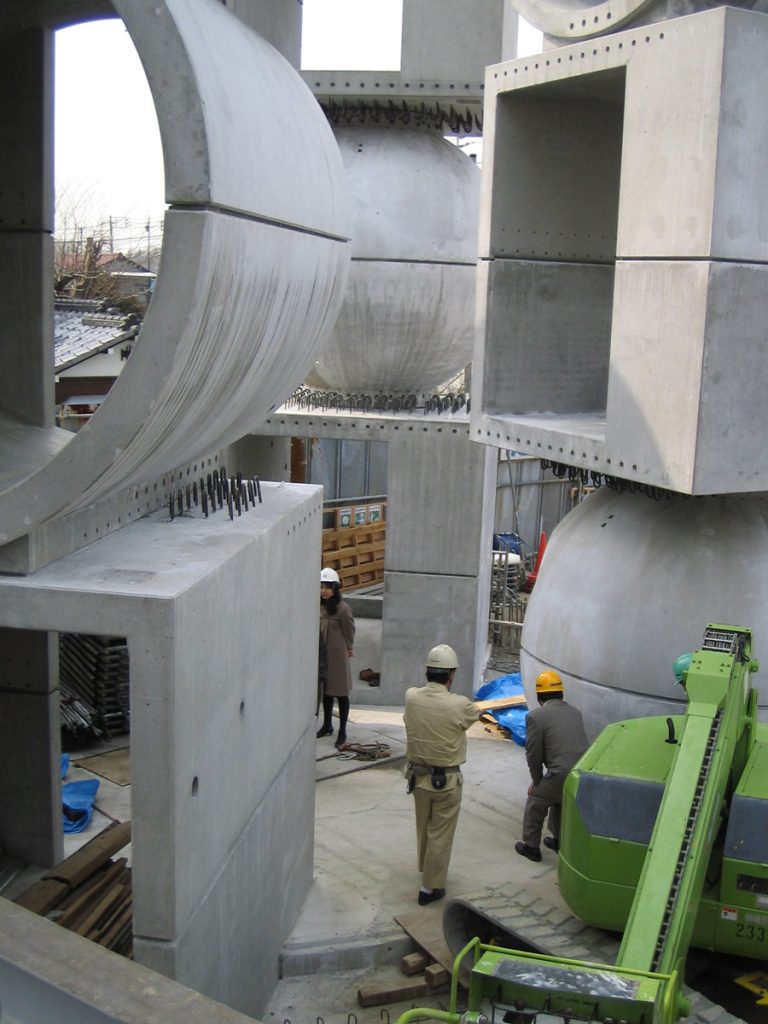
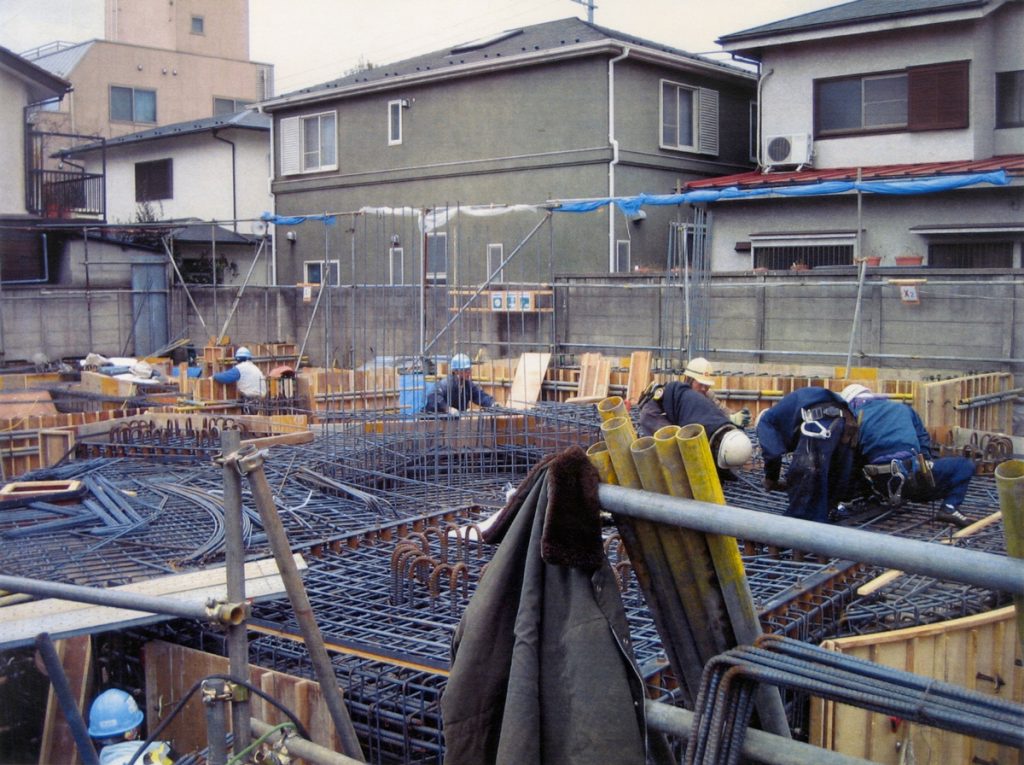
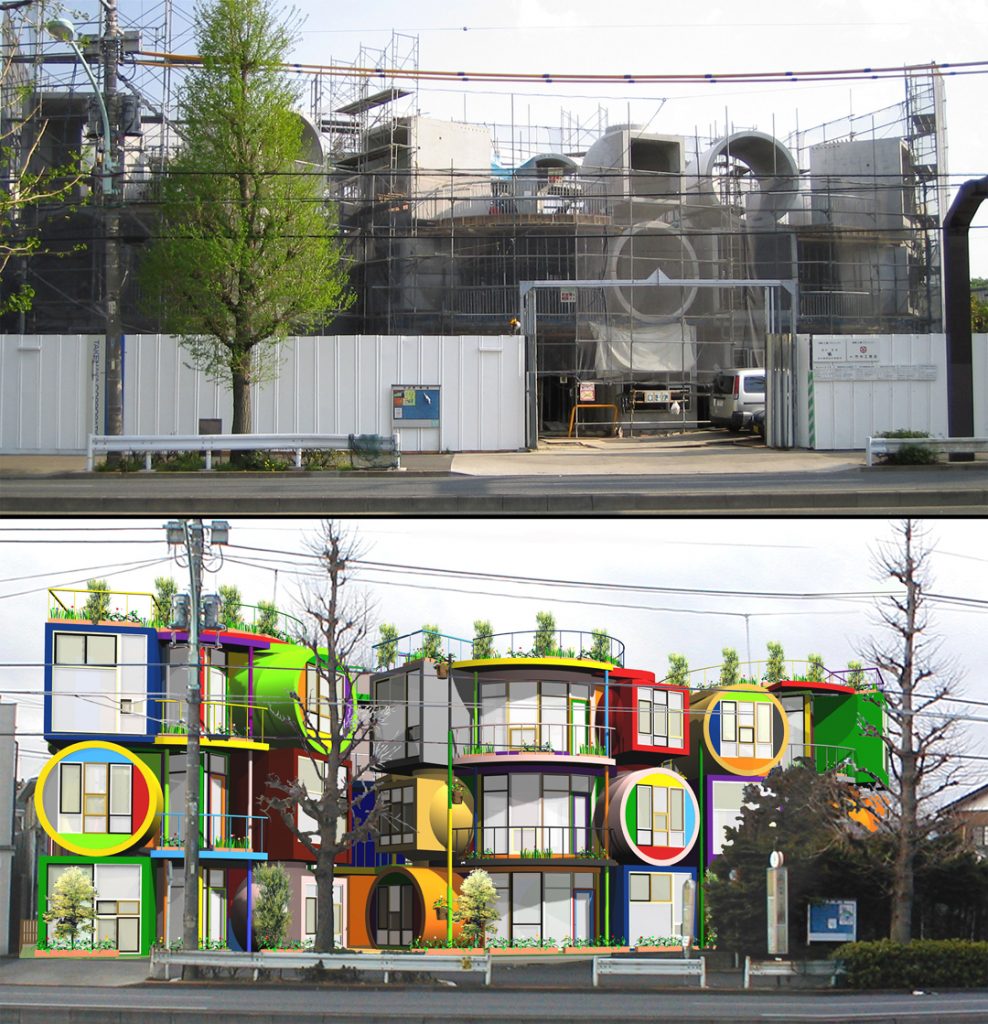



At its birth, the Mitaka Lofts was received as an eccentric artwork and a curious erection in the middle of a residential neighborhood in Tokyo. While it still stands out when viewed from the street with its vibrant colors and whimsical shapes, it has gained the respect and affection of those who have resided/reside there and have participated in various events and programs. It is a building that continues to live and grow with every person’s unique experience and is a place where anyone who enters becomes the main character in the story of the “making of”.




**The ARAKAWA+GINS Tokyo Office already launched a crowdfunding campaign last month to raise funds for the first phase of this long-term project through the platform Motion Gallery based in Japan. Since the system doesn’t readily support donations coming from countries other than Japan, we are preparing a separate platform for English-speaking people to participate in the project.
**Madeline Gins and Arakawa, Architectural Body (Tuscaloosa and London: University of Alabama Press, 2002), xi–xii.
